Advanced air fed gasification technology developed by EPR enables the rapid and near complete conversion of carbonaceous materials, such as biomass waste, to a low Btu fuel gas. This gas can then be combusted in a LoNOx burner to produce steam for district heating or cooling, industrial processes, or for generation of electrical power.
Depending on the overall waste derived fuel moisture, ash content and calorific value, the process generates just under one MWh of electrical energy for every metric ton of fuel introduced. Air emissions from the process are exceedingly low, allowing power plants up to 100 MW (nameplate) to operate under USEPA synthetic minor source air permits. Residual solids from the process are inert and carbon free and can be used for construction fill or landfill daily cover.
- Overall, the process is comprised of the following steps:
- Sorting of solid waste
- Processing of solid waste into Refuse Derived Fuel (RDF)
- Gasification of the processed RDF
- Generation of electricity using the fuel gas to produce steam for the turbine generators
- Treatment and clean-up of flue gas from the boiler prior to release to the atmosphere.
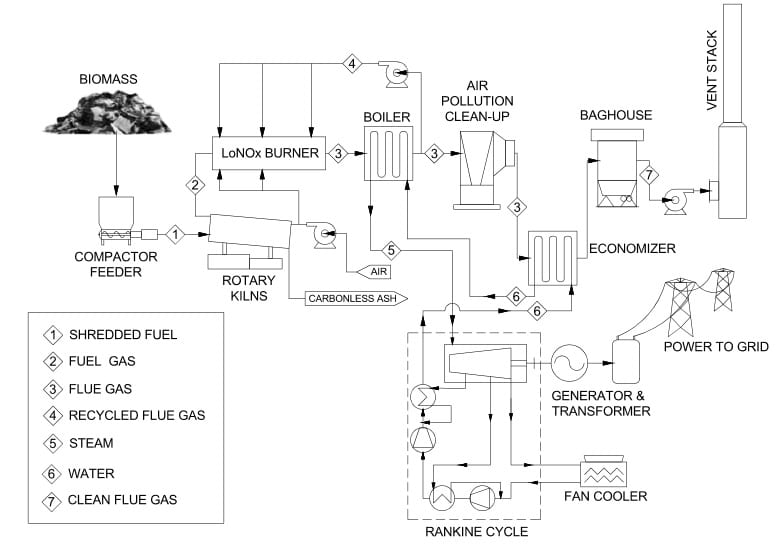
Shown below is a process flow diagram for a typical EPR waste to energy gasification line. Major process streams are identified by number in the table at the lower left. For more information on EPR patented and patent pending gasification technologies, see the Technology White paper accessed from the Library menu.
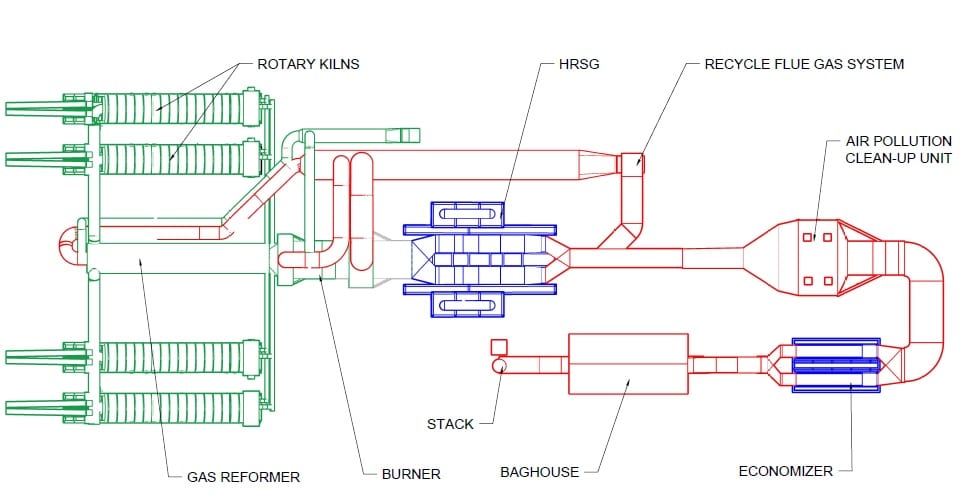
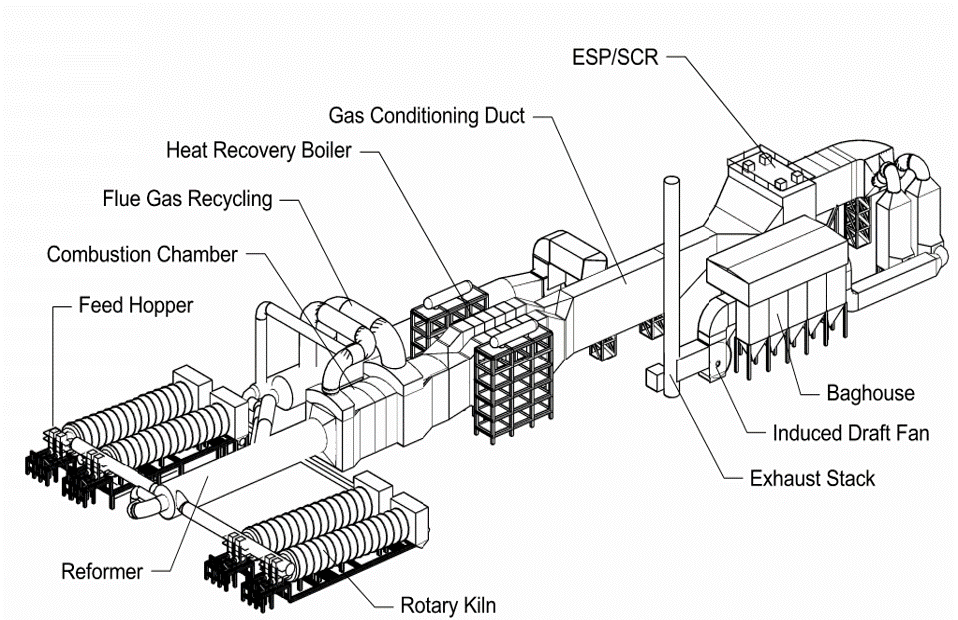
Rotary Kiln Systems

Rotary kiln gasifiers are a proven technology that is considered robust and dependable. EPR gasifier systems are comprised of a primary rotary kiln reactor, a reformer and LoNOx burner, heat recovery steam generator, flue gas treatment units and a control system. Rotary kiln gasifiers can be specifically designed to operate on biomass, mixed combustible solid waste, and certain hazardous solid wastes.
The operating temperature of primary rotary kiln reactor is normally in the range of 1,000 °C. The steel kilns units are refractory lined with an insulating castable and a hard refractory which can be operated up to temperatures of 1400 °C.

Rotary kilns have the advantage of being able to operate over a wide temperature range, depending on the design and refractory used, and can handle a variety of waste components.
Rotary kiln systems are normally used at scales of approximately 50 to 200 tpd in a waste treatment capacity. For solid waste application, these gasifiers systems have a specially designed reformer and LoNOx burner to assure maximum oxidation and minimal particulate emissions. They can be fitted with various options for emissions control, heat recovery to steam, hot water, and electricity. Rotary gasifiers can be built in modules comprised of multiple kilns each, connected to a single reformer and LoNOx burner unit, boiler and air pollution control system.